Treating tooth decay is essential to stop the gradual erosion of tooth enamel, which can lead to tooth decay and a variety of dental problems.
Join Blissfulhealth to discover the causes, symptoms and effective treatment options to stop the progression of tooth decay and protect your oral health. Join us to discover ways to maintain a healthier smile.
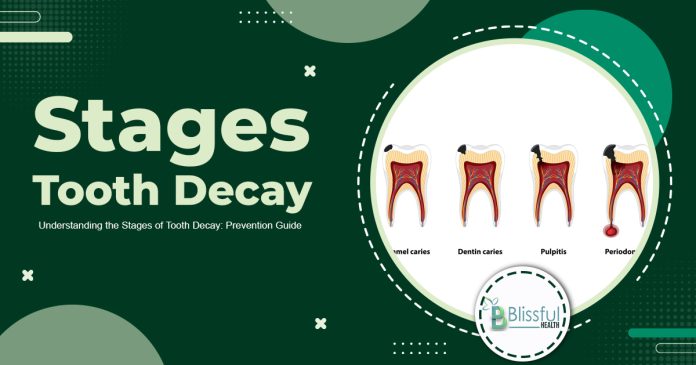
The Stages Of Tooth Decay
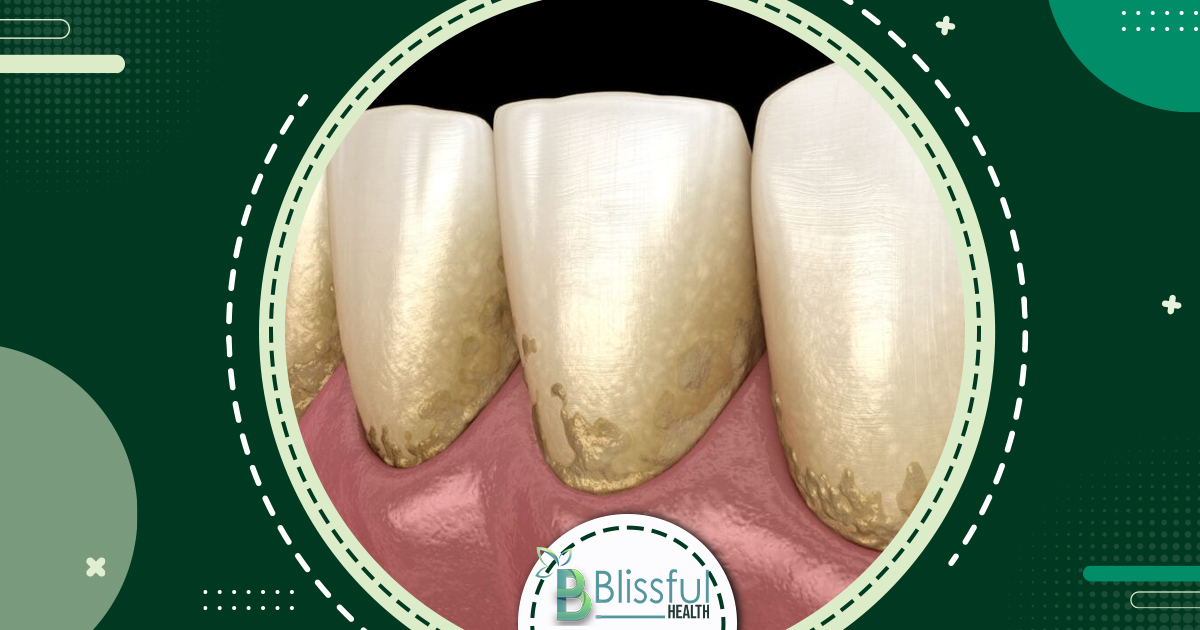
Plaque accumulation leads to demineralization, where teeth lose calcium due to bacterial action on ingested sugar, releasing acid onto the enamel. This causes white spots on teeth. Treatment involves fluoride application for remineralization, strengthening tooth enamel.
Stage 1: Plaque Accumulation And Bacterial Growth
Fluoride treatments like fluoride toothpaste, fluoridated water, or professional dental treatments help replenish lost minerals, strengthening enamel.
Treatment
Fluoride treatments like fluoride toothpaste, fluoridated water, or professional dental treatments help replenish lost minerals, strengthening enamel.
Stage 2: Enamel Demineralization
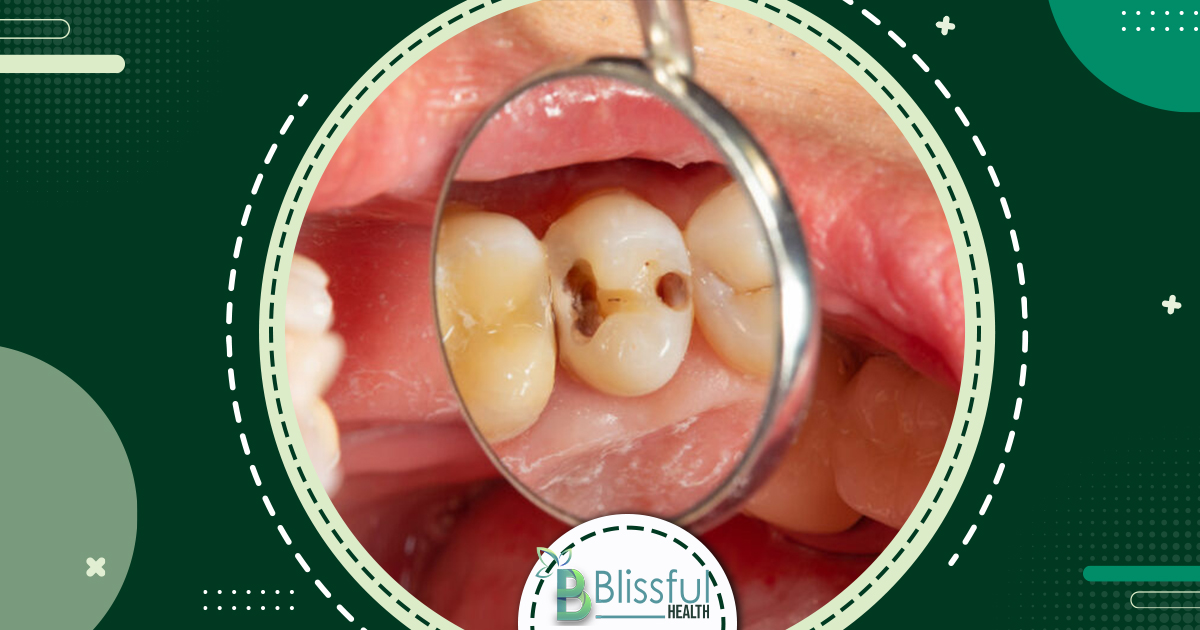
If demineralization persists, bacteria continue attacking enamel, causing decay and brownish discoloration. Left untreated, it progresses to cavity formation.
Treatment
Dental fillings are effective in treating decayed enamel. The affected portion is removed and filled with resin, ceramic, or dental amalgam.
Stage 3: Dentin Decay
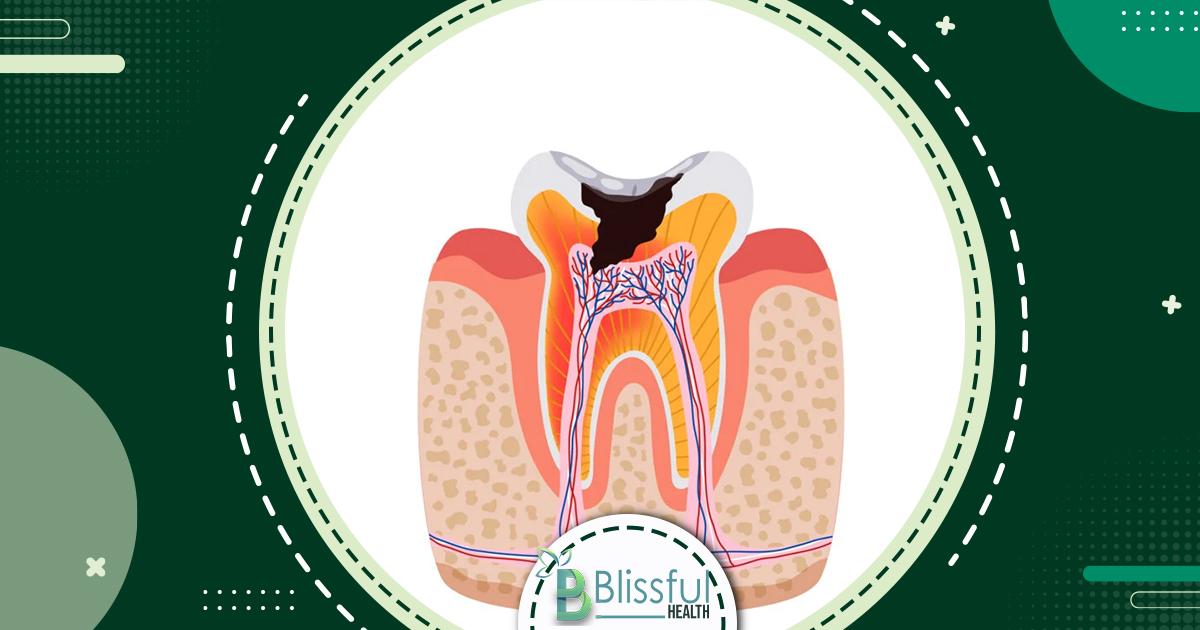
Untreated enamel decay progresses to dentin, a softer layer beneath enamel, causing heightened sensitivity to temperature and sugary foods.
Treatment
Treatment ranges from fillings to crown placement, depending on the extent of decay.
Stage 4: Involvement Of The Pulp
Decay reaches the tooth’s center, causing intense pain as it affects blood vessels and nerves. A root canal procedure becomes necessary to remove infected pulp and protect the tooth with a crown.
Treatment
Root canal therapy involves removing infected pulp and placing a dental crown to protect the tooth.
Stage 5: Abscess Formation
Bacterial invasion leads to infection and abscess formation, risking damage to the jawbone and surrounding tissues.
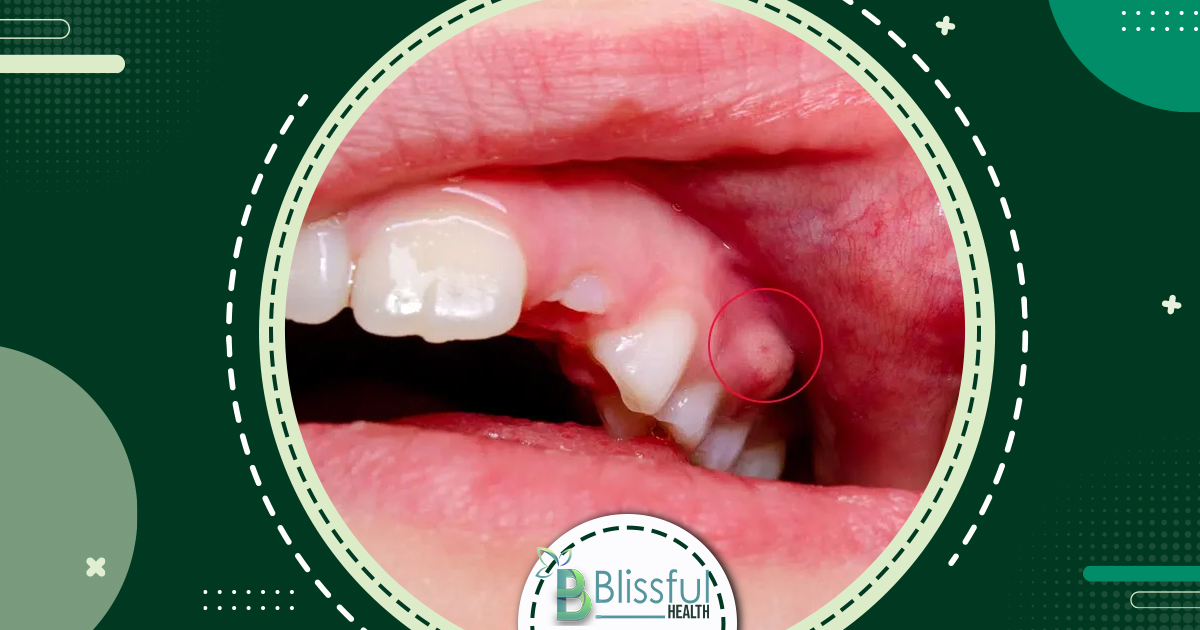
Treatment
Root canal or dental extraction may be necessary to prevent further complications.
Stage 6: Tooth Loss
Advanced decay or infection may lead to tooth loss, requiring replacement options like implants, bridges, or dentures.
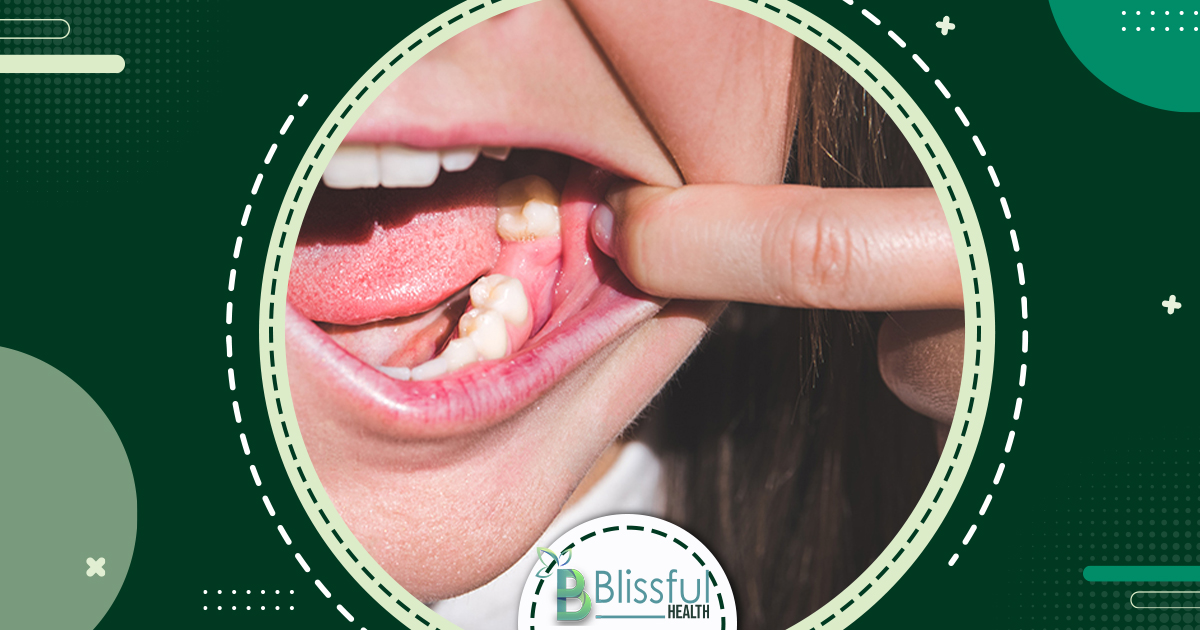

Treatment
Replacement options restore function and aesthetics, preventing shifting of remaining teeth and mitigating bite and jaw health issues.
Stage 7: Impact On Overall Health
Tooth decay can exacerbate health issues like diabetes and heart disease due to oral infections.
Treatment
Comprehensive treatment involves collaboration between dental and medical professionals to manage both oral and systemic health issues.
See More: Tooth Decay Treatment Causes, Prevention, Remedies
Preventing Tooth Decay
Preventing tooth decay starts with halting plaque buildup. You can achieve this by:
- Brushing Your Teeth: Brush at least twice daily using fluoride toothpaste.

- Rinsing and Flossing: After consuming sticky, acidic, or carbohydrate-rich foods, rinse and floss to remove food debris, especially after indulging in chocolate or citrus fruits.
- Interdental Cleaners and Floss: Utilize interdental cleaners and floss to eliminate food particles effectively.
- Fluoride Mouthwash: Incorporate fluoride mouthwash into your oral hygiene routine to eliminate plaque.

- Dental Sealants: Consider getting dental sealants on molars to shield them from decay.
- Fluoride Water: Drink fluoride water to strengthen tooth enamel.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist annually for checkups and professional cleaning.

Monitoring your diet is crucial for preventing tooth decay. Avoid acidic carbonated beverages and limit consumption of sweet, sticky snacks like candy bars and caramel. If you do indulge, brush immediately afterward to minimize the risk of decay. Remember, delaying brushing after consuming such foods increases the likelihood of tooth decay.
Conclusion
In summary, cavities are caused by bacteria in plaque on your teeth, where sugars from food are converted into acids, leading to tooth damage. With seven stages of progression, early detection is crucial as initial stages can be reversed, while later stages may cause irreversible harm.
Treatment options vary depending on the stages of tooth decay, ranging from fluoride treatments to fillings and root canals. However, prevention is still the best approach. Simple steps like regular brushing, avoiding sugary foods, and keeping up with dental check-ups play a critical role in preventing cavities. By prioritizing oral hygiene and proactive dental care, you can protect your teeth and maintain optimal oral health.