Blissfulhealth emphasizes the importance of quickly dealing with any signs of eye discomfort, redness, or itchiness, as they might indicate the start of eye infections, which in serious cases could lead to vision problems. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider to figure out what’s causing the issue and to get the right treatment.
What Is an Eye Infection?
An eye infection occurs when the eye is afflicted by microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi. The most prevalent type is pink eye, also known as conjunctivitis. Eye infection symptoms can include redness, irritation, discharge, and blurred vision.
Pink eye is predominantly caused by viruses, although bacteria can also be responsible. It’s important to note that antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections. However, bacterial eye infection, such as a stye eye infection, requires specific treatments.
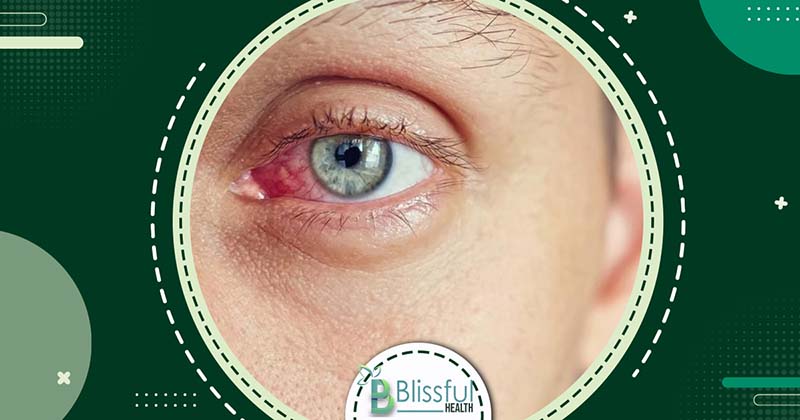
Eye infections can manifest in one or both eyes. While some infections are minor, others necessitate immediate medical attention as they can lead to vision impairment. Eye infection treatment varies depending on the cause and severity, and it’s crucial to know how to treat eye infection properly. Eye infections can affect various parts of the eye, including the eyelid, conjunctiva, cornea, and external structures. Recognizing the symptoms of eye infection early can prevent complications and ensure prompt treatment.
Causes of Eye Infections
The main causes of conjunctivitis, or pink eye, include:
- Viruses
- Bacteria
- Allergens
Additional factors contributing to eye infections include:
- Exposure to chemicals
- Wearing contact lenses
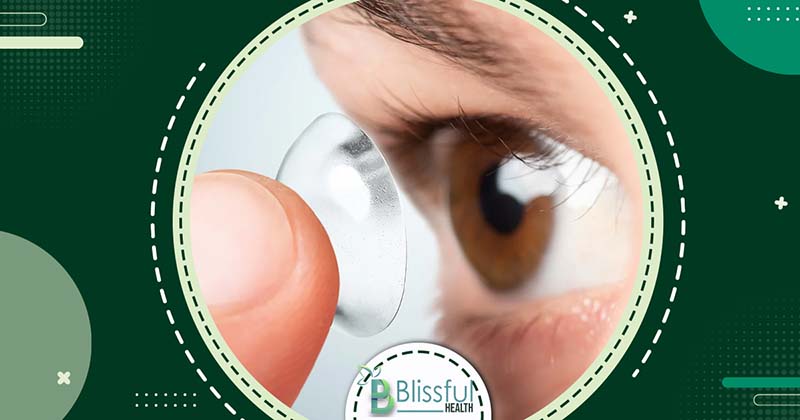
- Presence of foreign bodies in the eye, such as a loose eyelash
- Indoor and outdoor air pollution, such as smoke, dust, fumes, or chemical vapors

- Fungi
- Amoeba and parasites
Identifying the precise cause of conjunctivitis can be challenging due to overlapping symptoms regardless of the underlying cause.
Eye Infection Symptoms
Early indications of an eye infection may present as follows:
- Redness in the eyes
- Itching or irritation
- Eye pain

- Excessive tearing
- Swelling
Advanced symptoms of eye infections may include:
- Discharge from the eyes, often yellow and sticky
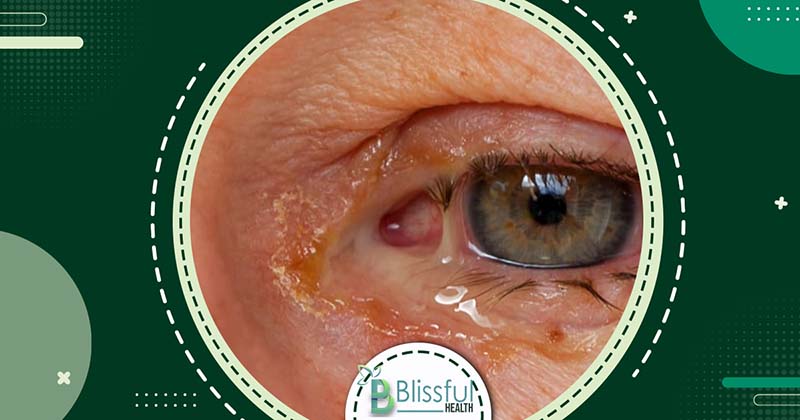
- Eyelashes clumping together due to discharge
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Blurred vision
- Fever
Eye Infection Treatments
The treatment for an eye infection hinges on its underlying cause. It may involve anti-infective medications administered in various forms, including eye drops, ointments, or tablets. Typically, antibacterial medications require 24 to 48 hours to take effect.
For viral or allergic infections, allowing them to resolve on their own may be necessary. However, you can enhance your comfort with the following home remedies:
- Applying damp, warm, or cool compresses to alleviate discomfort
- Using lubricating eye drops (artificial tears)

- Taking over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers
- Avoiding allergens that triggered the reaction initially
How to Prevent Eye Infections
To minimize the risk of eye infections or prevent the recurrence of viral infections, consider the following precautions:
- Avoid touching your eyes or face with unwashed hands.
- Maintain good hygiene by bathing regularly and washing your hands frequently.
- Adopt an anti-inflammatory diet to support overall health.
- Use clean towels and tissues when tending to your eyes.
- Refrain from sharing eye and face makeup with others.
- Launder your bedsheets and pillowcases at least once a week.
- Ensure your contact lenses fit properly and visit your eye doctor regularly for check-ups.
- Disinfect contact lenses daily using contact solution.
- Steer clear of direct contact with individuals who have conjunctivitis.
- Replace any object that has come into contact with an infected eye promptly.
Common Eye Infections Explained
Following a consultation with your doctor, they may identify the specific infection you’re experiencing, using medical terms such as:
- Pinkeye (conjunctivitis): Characterized by an infection of the conjunctiva, resulting in a pinkish tint to the eyes. It can stem from bacteria, viruses, allergic reactions, or irritants. Pinkeye often accompanies a cold, with viral causes being more common in adults and bacterial causes prevalent in children.
- Keratitis: Inflammation of the cornea, which can be triggered by bacteria, viruses, or waterborne parasites. Individuals who wear contact lenses are particularly susceptible to this condition.
- Stye: Painful red bumps that develop under the eyelid or at the base of eyelashes due to infection of the oil glands by bacteria. Resembling pimples, styes are not contagious.
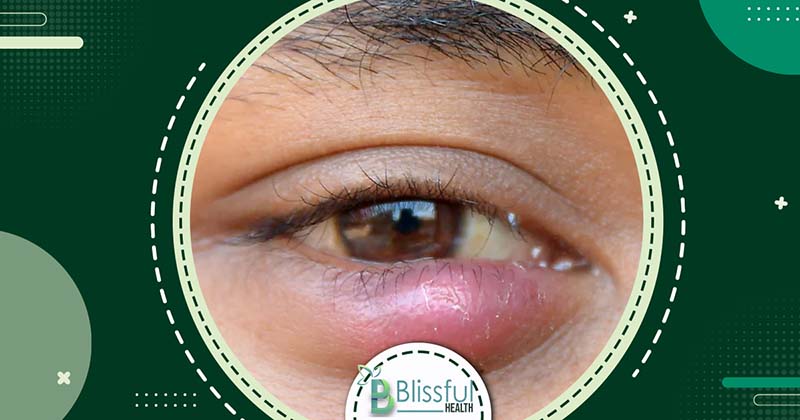
- Fungal Eye Infections: While rare, fungal eye infections can be severe. They often occur post-eye injury, especially if the eye was scratched by plant matter like a stick or thorn. Improper cleaning of contact lenses can also lead to fungal infections.
- Uveitis: Inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye. While certain viruses like herpes can cause uveitis, it’s more commonly associated with autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
Prevalence of Eye Infections
Eye infections are widespread, with approximately 1 million individuals in the U.S. seeking medical attention for them annually. A significant portion of these cases occurs among individuals who wear contact lenses.
Conclusion
Symptoms of eye infection typically subside on their own within a few days. However, if you experience severe eye infection symptoms, it’s imperative to seek emergency medical attention. Pain or loss of vision warrants prompt consultation with your doctor. Early intervention, including understanding how to treat eye infection, is key to minimizing the risk of complications associated with bacterial eye infection or stye eye infection. Proper eye infection can prevent the condition from worsening and ensure a speedy recovery.


